В журнале The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (IF=5,7) опубликована статья с участием сотрудников Лаборатории магнитной радиоспектроскопии НИОХ СО РАН: к.х.н., снс А.В. Шернюкова, к.х.н., снс В.М. Тормышева и д.х.н., проф. Е.Г. Багрянской (директор Института):
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Using Electron Spin Cluster
Raj K. Chaklashiya, Asif Equbal, Andrey Shernyukov, Yuanxin Li, Karen Tsay, Quentin Stern, Victor Tormyshev, Elena Bagryanskaya, and Songi Han
J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 20, 5366–5375
Publication Date:May 12, 2024
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00182
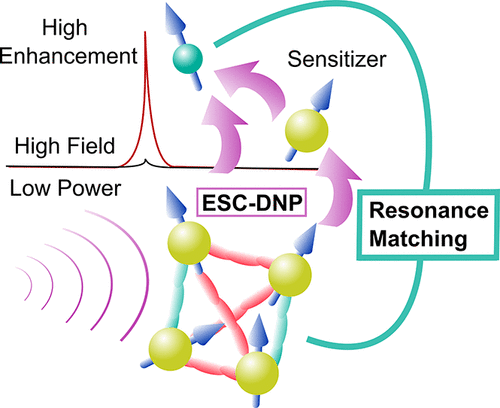
Abstract
Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) utilizing narrow-line electron spin clusters (ESCs) to achieve nuclear spin resonance matching (ESC-DNP) by microwave irradiation is a promising way to achieve NMR signal enhancements with a wide design scope requiring low microwave power at high magnetic field. Here we present the design for a trityl-based tetra-radical (TetraTrityl) to achieve DNP for 1H NMR at 7 T, supported by experimental data and quantum mechanical simulations. A slow-relaxing (T1e ≈ 1 ms) 4-ESC is found to require at least two electron spin pairs at <8 Å e–e spin distance to yield 1H ESC-DNP enhancement, while squeezing the rest of the e–e spin distances to <12 Å results in optimal 1H ESC-DNP enhancements. Fast-relaxing ESCs (T1e ≈ 10 μs) are found to require a weakly coupled narrow-line radical (sensitizer) to extract polarization from the ESC. These results provide design principles for achieving a power-efficient DNP at high field via ESC-DNP.
Альметрики:
Метрики PlumX теперь доступны в Scopus: узнайте, как другие ученые используют ваши исследования

