На сайте журнала Bioorganic Chemistry (IF 4,5) опубликована статья, соавторами которой являются ученые из НИОХ СО РАН - из лаборатория медицинской химии: к.х.н., снс С.С. Патрушев и д.х.н., проф. , гнс Э.Э. Шульц; научный сотрудник группы рентгеноструктурного анализа Т.В. Рыбалова; старший научный сотрудник группы ядерно-магнитного резонанся к.х.н. В.И. Краснов, старший научный сотрудник группы экологических исследований и хроматографического анализа к.х.н. Е.И. Черняк.
Synthesis and exploration of anticancer potential of spirocyclic 1,2,3-triazoline and aziridine derivatives of natural eudesmanolide isoalantolactone
Sergey S. Patrushev, Daria O. Kichkina, Arseny D. Moralev, Tatyana V. Rybalova, Vyacheslav I. Krasnov, Elena I. Chernyak, Marina A. Zenkova, Andrey V. Markov, Elvira E. Shults
Bioorganic Chemistry, Available online 6 January 2025, 108124
DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108124
Highlights
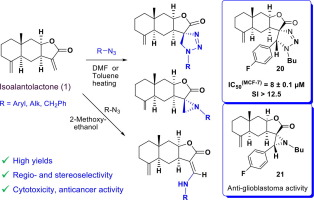
- Dipolar cycloaddition of isoalantolactone with azides on the exocyclic double bond.
- Spirocyclic structural entities on exocyclic double bond enhanced the cytotoxicity.
- Structure of new type of spirocyclic compounds was established by X-ray crystallography.
- Spirotriazoline derivatives of isoalantolactone are induced of the ROS-dependent death of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells via mitochondrial apoptosis.
- Spiroaziridine derivative of isoalantolactone exhibited synergistic cytotoxicity in combination with temozolomide.
Abstract
Eudesmane-type sesquiterpene lactone isoalantolactone 1 is of great interest due to its availability, biological activity and synthetic application. Respective series of original spirocyclic (11S,5ʹ) (1,2,3-triazoline-eudesma-4,15-enolides) and (11S)-aziridine-eudesma-4,15-enolides were efficiently synthesized via a chemoselective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of organic azides to the exocyclic double bond of the lactone ring of isoalantolactone or 13E-(aryl)isoalantolactones by heating in DMF or toluene. The thermal reactions of isoalantolactone with benzyl azide, 2-azidoethanol, or n-butyl azide in 2-methoxyethanol afforded 13-(alkyamino)isoalantolactones formed as a mixture of (Z) and (E)-isomers. The results of in vitro biological assays showed that novel spirocyclic isoalantolactone derivatives exhibited cytotoxicity against human breast cancer and glioblastoma cells at low micromolar concentrations. The most cytotoxic and selective (11S,5ʹ)-spiro-1,2,3-triazoline from 13E-(fluorophenyl)isoalantolactone 20 (IC50(MCF-7) = 8 ± 0.1 µM, SI(MCF-7) > 12.5) was found to induce ROS-dependent death of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells via mitochondrial apoptosis. The corresponding (11S)-spiroaziridine derivatives 21 at non-toxic concentrations (10 and 20 µM) effectively suppressed motility, clonogenicity and adhesion of glioblastoma cells and exhibited synergistic cytotoxicity in combination with temozolomide. In silico analysis revealed the potential ability of the 13-aryl (11S)-spiroaziridine derivative 21 to bypass the blood–brain barrier and exhibit anti-glioblastoma activity probably based on the direct interaction with Hsp90α.
Graphical abstract