В журнале Dyes and Pigments ( IF 4,1) по результатам работы, выполненной совместно с коллегами из Института физики им. Лебедева, Института органической химии им. Зелинского и МГТУ им. Баумана, опубликована статья, соавторами которой является сотрудники Института: к.х.н. Е.А. Радюш (нс, ЛГетС), к.х.н. Е.А. Чуланова , к.х.н. И.Г. Иртегова (снс, ЛЭАСМ), к.х.н. И.К. Шундрина (снс, ЛЭАСМ), Е.А. Франк, к.х.н. Н.А. Семёнов, д.х.н. Л.А. Шундрин (завлаб ЛЭАСМ) и д.х.н. А.В. Зибарев (г.н.с., ЛГетС)
Polycyclic 1,2,5-chalcogenadiazole dyes: structural, optical, and redox properties in neutral and radical-ion states (chalcogen = S, Se)
Ekaterina A. Radiush, Vladislav M. Korshunov, Elena A. Chulanova, Lidia S. Konstantinova, Alexey I. Ferulev, Irina G. Irtegova, Inna K. Shundrina, Ekaterina A. Frank, Nikolay A. Semenov, Ilya V. Taidakov, Oleg A. Rakitin, Leonid A.Shundrin, Andrey V. Zibarev
Dyes and Pigments, Volume 242, November 2025, 112922
DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2025.112922
Highlights
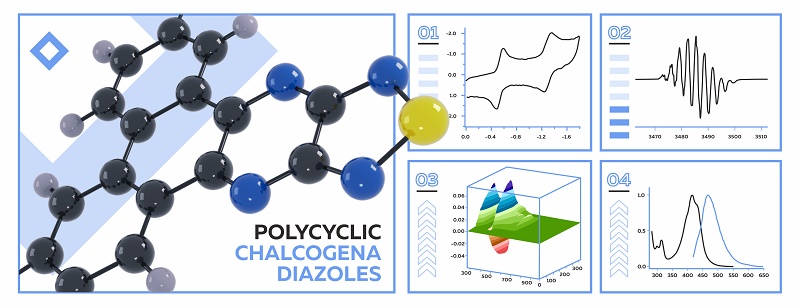
- π-extended 1,2,5-thia/selenadiazoles are promising organic dyes for optoelectronics .• they are thermally stable in the solid state and solution • their absorption, emission and redox properties are tunable • their chemically and electrochemically-accessible radical-anion state is stable • emission from the radical-anion state embraces near-infrared area
Abstract
Graphical abstract
Due to thermal, structural, optical, and redox properties in neutral and radical-anion states, synthetically easily-available polycyclic 1,2,5-chalcogenadiazoles (chalcogen = S, Se) are promising π-dyes/non-fullerene electron acceptors for organic optoelectronics.
ТЕКСТ PDF